Blockchain Technology
Master the basics of Blockchain Technology and understand how it is ruling the world!
Imagine 💭 that you are in your favorite fashion store 🏪 , and you scan the QR code for the dress 👗 you want to buy 💵 . As soon as you scan the code, you can view all the details about where the fabric was cleaned, colored, woven, designed, etc. What if you could also track supply and distribution 🚚 to figure out how it was delivered, how long 🕑📅 it took to get to the store, and so on?

Could there be a technology 👩💻 that can assist in recording data 🧾 at each step and making that data clearly available to all? 🌐
Welcome to the Blockchain universe! 🙌
Today, each transaction 💲 performed is recorded in a book 📕, ledger, spreadsheet, or database. However, this transaction is private and centralized. Blockchain offers a growing list of records 📚 at each step of the transaction linked 🔗 among themselves as nodes and is decentralized and open to all 🌐 . Blockchain technology combines public transparency with privacy protection to create a single data platform.
🚩 Let us see the definition of Blockchain,
Blockchain is a distributed 🌐, decentralized peer-to-peer ledger (record of transactions) that is duplicated across numerous nodes (computers) 💻 in a network, allowing data about any event or transaction 🔃 to be recorded in real-time 🕑📅 . It is a chain 🔗(nodes) made up of blocks 🟥 that are used to record digital assets 🔢 with the help of a secure algorithm 👩💻. By design, blockchains are immutable and immune to the modification of data.
This network 🌐 of computers 💻 manages the Blockchain without the use of a hierarchy 🔺. Blockchain networks are commonly referred to as peer-to-peer networks because of their flat architecture.
These computers 💻 check each transaction 🔃 individually before adding them to a 'block' 🟥 of data. These blocks are then uploaded to the Blockchain and downloaded to each machine 💻.
Dissecting the word BLOCKCHAIN
Block 🟥
Like a page 📄 in a record book 📕, each block stores a number of transactions. Each block is connected to one before and after it.
Chain 🔗
Hashes – sequences of numbers 🔢 and characters — are used to record these transactions. Each transaction's hash is created using the previous transaction’s hash. This generates a chain effect 🔗, making it impossible to modify the order of hashes. As a result, once a transaction has been added, it cannot be changed.
What distinguishes a Blockchain ledger from a database? Isn't it the same thing when it comes to capturing, organizing, monitoring, and regulating data? 🤔
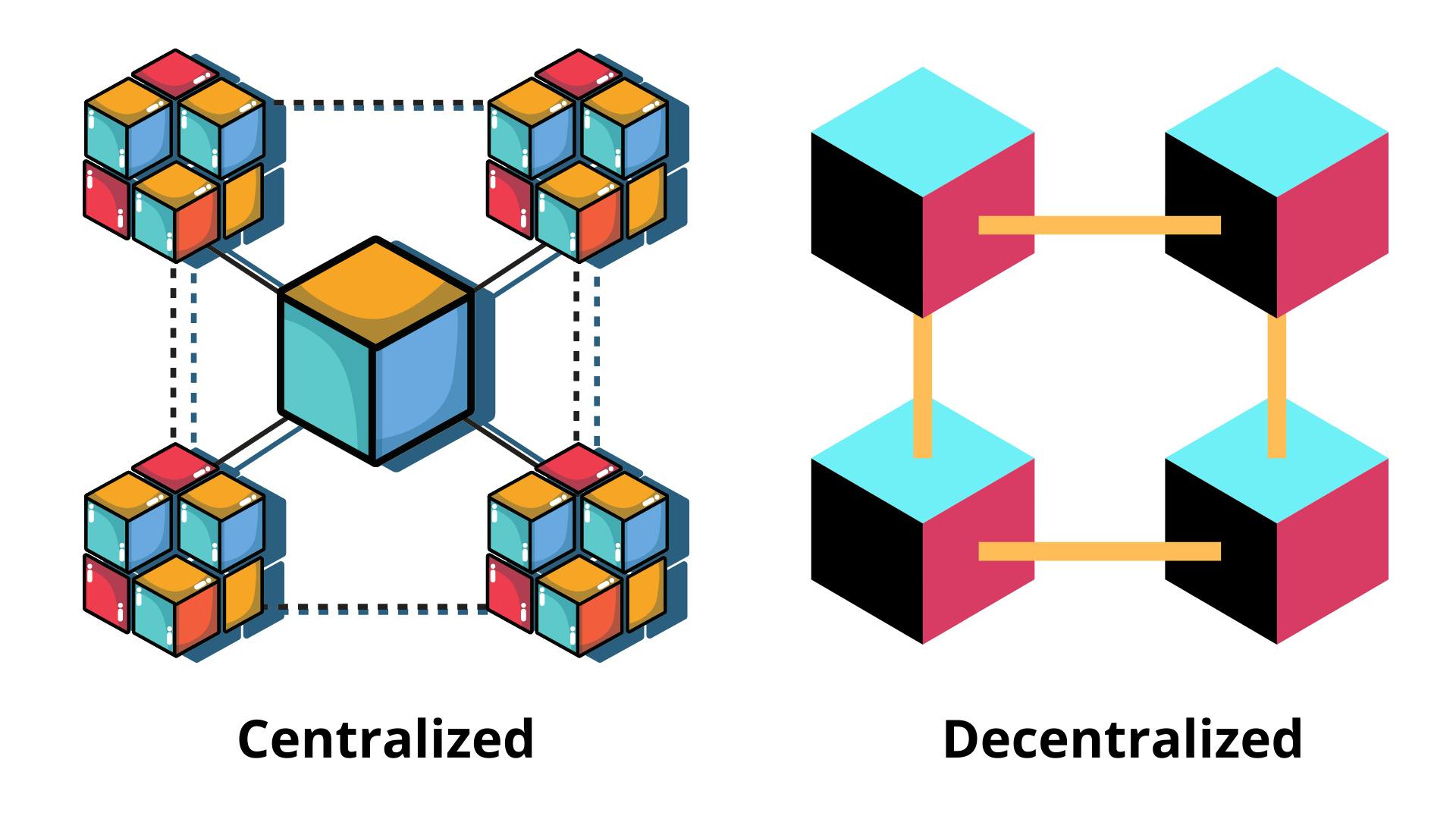
- Hashes of the transactions 🔃 are transparent to all the nodes in the network 🌐 .
- Blocks have specific storage 💾 capacities and, when filled, are closed and linked 🔗 to the previously filled block 🟪.
- A central authority, a firm, or a government organization 🏢 owns databases. On the other hand, Blockchain is a peer-to-peer network, where one node may communicate with any other node 🖥 .
Terminologies used in Blockchain
🚩 Let us familiarize ourselves with important terms before digging deep into the Blockchain.
Ledger
Payments 💵, supply chain details, health records 🧾, real estate contracts 🏬, and other transactions are all recorded in a book(digitally) 💻.
SHA-256
SHA-256 is a cryptographic algorithm 👩💻 that accepts any input length and gives an output of 256-bit or 64-character hash. SHA-256 hashing algorithm assures that the original information cannot be deduced from the hash output, making it very safe 🤩.
Hash
A hash is a shortened digital signature of the data. Hashes are sent over a public network 🌐. Each block 🟨 uses a hash function to refer to the previous block 🔗.
Mining
Mining ⛏ on the Blockchain is a means of verifying each transaction 🔃 stage. Blockchain miners 👩🏭 are the individuals 👨🏭 involved in this process. Before adding new a new block, all miners need to solve complex mathematical problems 🔢 to calculate hashes. The miner receives a reward 💰 as a cryptocurrency(bitcoin) and the transactions are added to the Blockchain once the miner's solution has been confirmed ✔.
Node
Any computer 💻 that is part of a peer-to-peer network and maintains a copy of the Blockchain is referred to as a node in a blockchain.
Merkle Tree
Merkle tree, also known as "hash binary tree," is a data structure that is used for storing transactions 🔃 on a blockchain efficiently.
Decentralization
Decentralization in the Blockchain is the transfer of control of any activity to a distributed network 🌐, unlike a centralized organization that has full control over your activities.
Benefits of Decentralization 🤩 :
In the form of a distributed ledger, each network member owns a copy of the same data 📕.
Companies 🏢 frequently share information with their partners 🤝. Each time data is modified, the possibility of data loss or inaccurate data entering the workstream increases 🤯. Thanks to decentralized data storage 🤗 , every entity has access to a real-time 🕑📅 , shared view of data.
Decentralization can help mitigate sources of vulnerability in systems where there might be an excess of dependence on explicit workers 👨🏭.
Decentralization may also aid in resource distribution optimization, ensuring that promised services are delivered with improved performance 💯 and consistency ✔ .
How does a Blockchain work 🤔
The purpose of Blockchain is to make digital information 💾 accessible by allowing it to be recorded and shared but not altered.
Blockchain technology is a combination of three cutting-edge technologies 🤩 :
- Cryptographic Algorithms 👩💻
- A distributed ledger peer-to-peer network 🌐
- A mechanism for keeping network transactions and records on a computer 💻
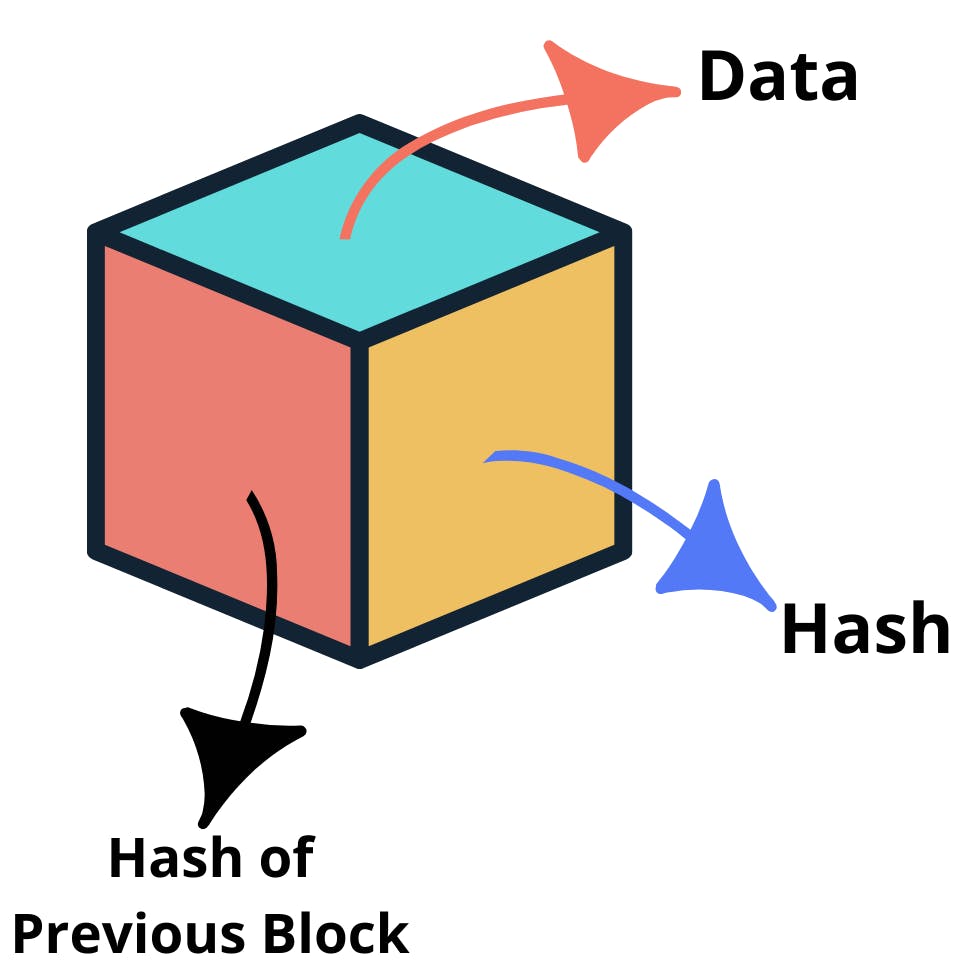
Each block contains some data, the hash of the block, and the hash of the previous block.
- DATA: It depends on the type of blockchain, for instance, a bitcoin.
- HASH: You can compare a hash to a fingerprint. It identifies a block 🟥 and is always unique. Once a block is created, its hash is calculated 🔢. Changing something inside the block will cause the hash to change.
- HASH OF PREVIOUS BLOCK: This hash is used while calculating the hash of the current block which effectively creates a chain 🔗 of blocks.
🚩 Now, let's take an example. Here we have a chain🔗 of 3 blocks 🟨 .
Let's assume you've tampered ❌ with the second block 🟧, which will change the hash of the block. As a result, block three and all subsequent blocks will be invalid ❌ since they will no longer retain a valid hash of the previous block. As a result, altering a single block invalidates all subsequent blocks 😮 .
To make your Blockchain legitimate ✔ again, you will have to recalculate 🔢 all the hashes of other blocks. These days, computers are extremely fast ⚡, capable of calculating hundreds of thousands of hashes per second 🕑 . This indicates that hashes alone are insufficient to prevent tampering 😐 .
To counteract this, Blockchains employ a mechanism ⚙ known as Proof-Of-Work. It's a method that increases the duration 🕑 of rebuilding blocks. This approach makes tampering with the blocks extremely difficult 🤯 because if you tamper with one block, you'll have to recalculate the Proof-Of-Work for all subsequent blocks. As a result, a Blockchain's security is derived from its innovative hashing and the proof-of-work process 💯 .
Since Blockchain is a peer-to-peer network 🌐, when someone joins this network, they get the full copy of the Blockchain.
🚩 Now let's see what happens when someone creates a new block 🟩 .
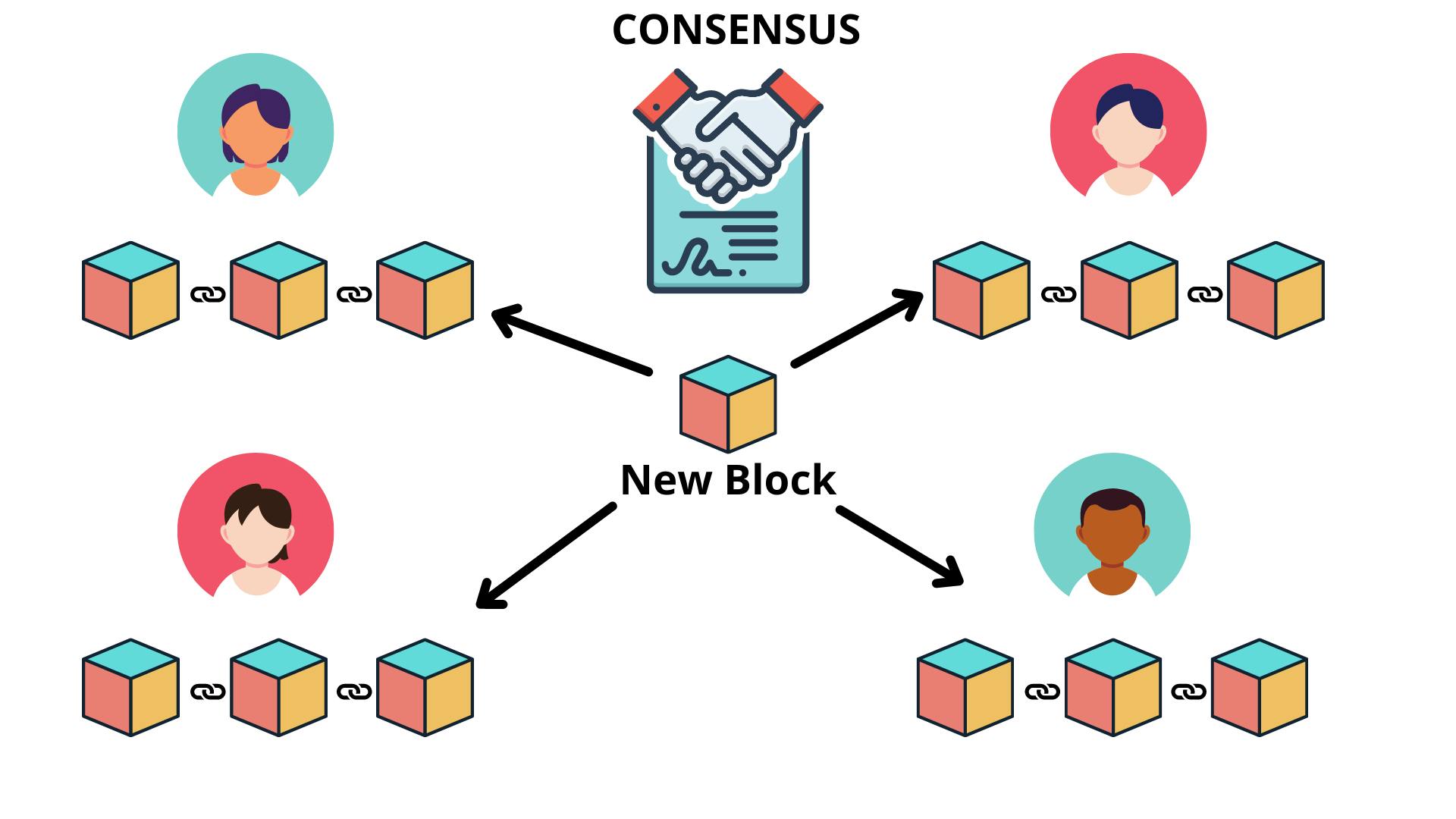
Everyone on the network receives 🌐 the new block 🟩 . Each node then verifies ✔ the block to ensure that it hasn't been tampered ❌, and uploads the block to each node 🖥. All the nodes in this network create consensus 🤝. They agree about which blocks are valid and which aren't.
Blocks that have been tampered with will be rejected ❌ by the network's other nodes. To effectively tamper with a Blockchain, you'll need to tamper with all of the chain's blocks, redo each block's proof-of-work, and gain control of more than half of the peer-to-peer network. Then and only then will your modified block be acknowledged by the rest of the world. This is nearly difficult to accomplish! 😎
HERE’S A SUMMARY OF HOW BLOCKCHAIN WORKS 💯:

Conclusion ✨
Blockchain is a very advanced technology 💯 that provides efficient verification ✔, regulation, transparency, and traceability of data 📄 . This technology can also be easily integrated with Big Data 📚 . Blockchain solutions can also help cut costs 💵 and eventually make many services more competitive.
Author of the blog:
Mohammad Amaan (Campus Chapter Guru - AI Probably)
